- Application - Heartbeat over TCP/IP (client)
Description how to run a heartbeat signal on DataMan using communication script.
Description how to run a heartbeat signal on DataMan using communication script.
This script establishes a communication channel to a host device (e.g. PC or PLC) and maintains the communication link via a heartbeat. The heartbeat process is where the DataMan reader sends a defined message (e.g. “HB”) to the host device periodically after fixed intervals. This is implemented using a Communication script, no Data Formatting script is required for the heartbeat function.
First the host device-DataMan communication is captured in the onConnect part of the script. It will handle the connection which is defined by the IP address of the host device and the port it connects on. Using the setTimer feature, it defines a timer. This setTimer feature also takes an argument as an input which is the time interval in seconds that the timer increments up to. When the timer reaches the value specified in the argument, this calls the onTimer function. It then sends the heartbeat message to the host and starts the timer from zero.
The following parameters are listed at the top of the script and are listed must be set as required for the application:
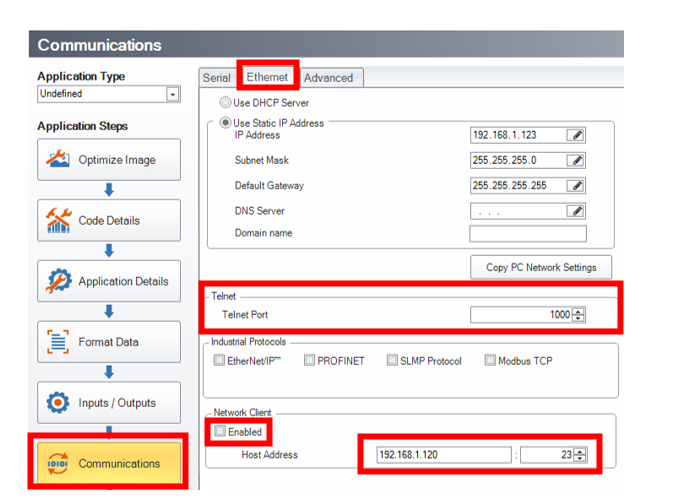
Communication Script:
'use strict';
// Enable/disable logging
const LOG = true;
const HB_IP = '192.168.0.100'; // IP address where to send the heartbeat (could be PLC, PC etc.)
const HB_CLIENT = false;
const HB_CLIENT_PORT = '1000';// Network Client port which DataMan communicates on
const HB_TELNET_PORT = '23'; // Telnet port which DataMan communicates on
const HB_TX_HEADER = '?'; // Define the header for message to host device
const HB_TX_FOOTER = '!'; // Define the footer for message to host device
const HB_TX_MSG = 'HB'; // Define the heartbeat message to send to host device
const HB_TIME = 10; // Define the time interval (in seconds) for sending the heartbeat message
let heartbeatHandler = null;
function CommHandler (localName) {
return {
onConnect: function (peerName) {
const sourceIP = peerName.substr(0, peerName.lastIndexOf(':'));
const peerPort = peerName.substr(peerName.lastIndexOf(':') + 1);
const localPort = localName.substr(peerName.lastIndexOf(':') + 1);
// If IP is the defined host IP address and specified port
if (sourceIP === HB_IP && ((peerPort === HB_CLIENT_PORT && HB_CLIENT) || (localPort === HB_TELNET_PORT && !HB_CLIENT))) {
heartbeatHandler = this;
logMsg(HB_IP + ': Connected');
this.setTimer(HB_TIME);
return true;
}
return false;
},
onDisconnect: function () {
if (this === heartbeatHandler) {
heartbeatHandler = null;
logMsg(HB_IP + ': Disconnected');
return true;
}
return false;
},
onError: function (errorMsg) {
},
onExpectedData: function () {
},
onUnexpectedData: function () {
},
onTimer: function () {
if (this === heartbeatHandler) {
heartbeatHandler.send(HB_TX_HEADER + HB_TX_MSG + HB_TX_FOOTER);
heartbeatHandler.setTimer(HB_TIME);
}
},
onEncoder: function () {
}
};
}
function logMsg (msg) {
if (LOG) {
console.log(msg);
}
}